
AI in Finance is transforming banking, investing, and risk management. Discover how algorithms shape money, trust, and the future of financial systems.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has quietly shifted from being a futuristic experiment to becoming the invisible engine driving global finance. From Wall Street algorithms making microsecond trades to mobile apps offering personalized financial advice, AI now influences how money flows across borders, how risks are calculated, and how trust is built in an increasingly digital economy.
For many readers, the challenge is not just understanding what AI is, but what questions to ask about it. How does it impact your bank account? Should you trust an algorithm with your investments? Will AI reduce risks or introduce new ones? This blog explores those queries, weaving them into real examples so you can understand both the technology and its personal consequences.
The Evolution of Digital Intelligence in Finance
Finance has always been about pattern recognition. In the past, traders stared at ticker tapes; today, machines parse millions of data points per second. Early automation focused on back-office efficiency, but AI takes it further — enabling predictive analytics, fraud detection, and self-learning investment strategies.
A key question readers often have is: How is AI different from the old systems banks already used? The difference lies in learning. Traditional models required human-designed rules; AI systems adapt from data, finding correlations humans cannot see. The journey began with statistical models in the 1980s, matured with algorithmic trading in the 2000s, and now enters a phase of explainable AI (XAI), where transparency becomes as critical as speed.
Banking Transformed by Algorithmic Decisions
Retail banking once relied on queues and paper forms. Today, chatbots like Erica (Bank of America) or EVA (HDFC) resolve millions of queries instantly. AI enables real-time credit scoring, transaction monitoring, and fraud detection.
Here’s a question most people don’t think to ask: When my loan or card is approved instantly, who made that decision — a person or a machine? Increasingly, it’s an AI model weighing income patterns, spending behavior, and even device fingerprints.
For banks, the advantage is deeper engagement. AI tracks anomalies and adjusts offers in real time. For customers, it means faster approvals, personalized offers, and better fraud protection.
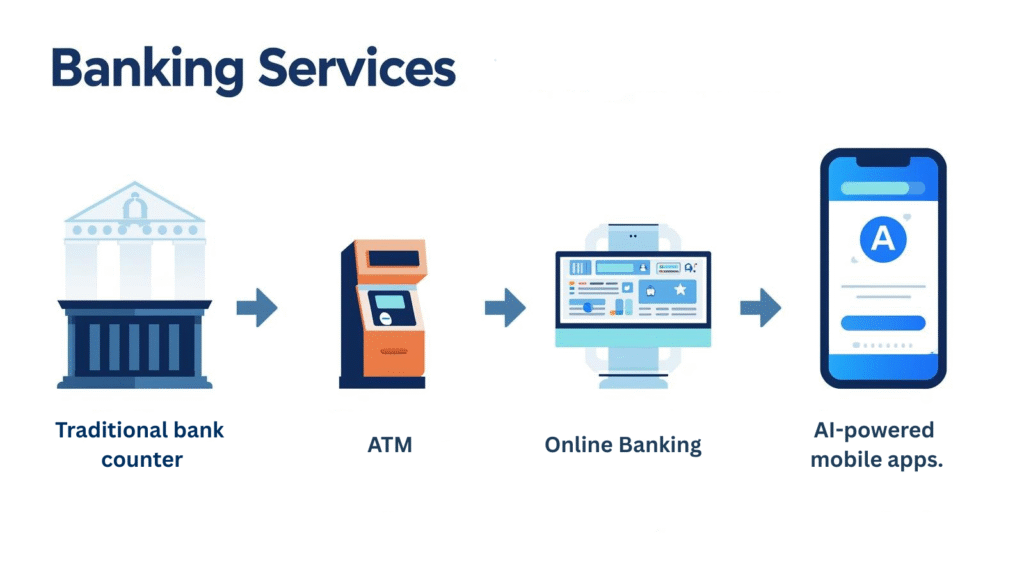
Everyday Life with AI-Powered Banking
AI in finance isn’t just about traders or bankers; it shows up in everyday lives. From instant credit approvals at checkout counters to fraud alerts that pop up while traveling abroad, the technology creates invisible guardrails around daily money use.
One question to ask is: How many of my daily financial interactions are already touched by AI without me realizing it? The answer is: almost all of them. Even when you swipe a card overseas or receive a suspicious login alert, algorithms are quietly working in the background. These subtle touchpoints build confidence, reminding us that finance is no longer a distant institution but an always-on companion in our pockets.
Investing in the Age of Machine Learning
Institutional investors pioneered algorithmic trading, but retail investors now benefit from robo-advisors like Betterment, Wealthfront, and Zerodha’s Nudge. These platforms democratize sophisticated portfolio management once reserved for wealthy clients.
A natural question arises: Should I trust an algorithm over a human advisor? AI offers scale, reduced bias, and lower costs. It analyzes vast datasets — earnings reports, news sentiment, geopolitical risks — and suggests portfolios in seconds. Yet human advisors still play a role in emotional reassurance and complex decision-making.
For markets, AI ensures liquidity and efficiency, though it also raises concerns of “flash crashes” when multiple algorithms overreact simultaneously.
Sharper Risk Management Through Predictive Models
Financial risk is as old as finance itself. But AI adds precision. Banks use machine learning to detect laundering patterns, insurers apply predictive analytics for claims, and hedge funds test scenarios across thousands of variables.
A question worth asking: Does AI make finance risk-free? The answer is no. It reduces some risks while creating new ones. Algorithms may be biased, misinterpret unusual data, or fail under conditions not present in their training. This is why regulators emphasize explainable AI (XAI).
A European bank reduced false positives in anti-money laundering alerts by 30% after deploying an AI-driven monitoring system. The savings ran into millions, but more importantly, it restored analyst confidence by showing why each flagged transaction was suspicious.
The Human Side of Algorithmic Decisions
Finance is not just about numbers — it’s about trust. People want to know why their loan was rejected, why their portfolio shifted, or why a payment was blocked. AI can deliver speed, but without transparency it risks alienating users.
Here, a hidden question emerges: If AI makes the call, can it explain itself? Customers are more willing to accept negative outcomes if the process feels fair and understandable. This is why explainable AI and human-AI collaboration matter as much as raw computing power.

Common Misconceptions About AI in Finance
AI will replace human bankers.
Reality: AI automates repetitive tasks, but relationships, ethics, and strategy remain human domains.
AI can guarantee profits in investing.
Reality: AI detects patterns but markets remain unpredictable, influenced by human and geopolitical events.
AI benefits only big banks.
Reality: Cloud-based AI tools make advanced analytics available to startups and smaller players.
These myths reflect questions people should be asking: What can AI really do, and what are its limits?
Global Rules Shaping Intelligent Finance
Governments and regulators are catching up. The EU’s AI Act, the SEC’s algorithmic trading guidelines, and India’s RBI framework for digital lending highlight accountability.
Readers often forget to ask: Who ensures AI in finance is fair? The answer lies with regulators and international bodies like the IMF and BIS. Yet global harmonization remains a challenge. A bank using AI in London, Singapore, and New York must navigate different frameworks, raising questions of consistency and fairness.
Case Study: Robo-Advisors and the Rise of Inclusion
Consider India, where millions of first-time investors entered markets during the pandemic. Traditional advisors couldn’t scale to guide them all. Robo-advisors filled the gap, offering automated, low-cost portfolios tailored to risk appetite.
Key question: Can AI expand financial inclusion? Yes — if combined with regulatory safeguards. In India, SEBI guidelines ensured transparency, building trust among small investors. This case shows how AI can empower new participants in global markets.
Behavioral Shifts in AI-Driven Investing
AI doesn’t just change systems — it changes us. Investors now log in more often, trust algorithmic nudges, and diversify earlier than previous generations.
The key question here: How is AI reshaping investor psychology? Behavioral economists note that AI reduces decision fatigue, but it also risks over-confidence in machine outputs. This balance between efficiency and dependency will define long-term wealth building.
The Next Horizon: Quantum Meets Finance
The next frontier is the fusion of quantum computing and AI. Quantum-enhanced algorithms could analyze portfolios beyond today’s capacity, unlocking new strategies in fraud detection and optimization.
The question readers should anticipate: What happens when quantum breaks current encryption? Banks are already preparing for post-quantum cryptography to secure financial transactions. The marriage of AI and quantum may define global finance beyond 2030.
Key Insights at a Glance
- AI in finance is no longer experimental; it drives everyday banking, investing, and compliance.
- Customers should ask how AI makes decisions and whether it can explain them.
- AI reduces risks but introduces new systemic vulnerabilities.
- Regulations are evolving, but harmonization is still a global challenge.
- The future lies in convergence with blockchain and quantum computing.
Explore More
- The Psychology of Money: 18 Hidden Secrets of Financial Success
- Why Financial Independence Beats Riches in the Long Run : Think Beyond 2025
- The Hidden Power of Compounding: 7 Proven Lessons for a Better Life
- Wealth Habits That Last: 10 Smart Money Systems for Life
- Financial Independence Mistakes: 8 Mistakes Holding You Back From True Freedom
- What is the FIRE Movement in India: 7 Powerful Secrets to Financial Independence
- What is FIRE Movement: 7 Powerful Secrets to Achieve True Financial Freedom – Ultimate Global Guide
- How to Stick to a Budget Without Feeling Restricted: 7 Proven Strategies
- SEBI:Money Matters : Let’s Understand
- AI-Powered Threat Intelligence: The Ultimate Double-Edged Sword in Cybersecurity
- 5 Ways Zero Trust Stops Hackers Cold
- Cybersecurity’s Fastest War: The Ultimate Battle When AI Fights AI Beyond 2025
- The Ransomware Epidemic: Why SMEs Are The New Primary Target
- What Is Vibe Hacking and How Is AI Using It? 5 Shocking Facts About the Threat to Our Trust
- IMF on AI and financial stability.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is AI in finance?
AI in finance means applying algorithms, machine learning, and natural language processing to banking, investing, and compliance. - How do banks use AI daily?
They use AI for fraud detection, instant loans, chatbots, compliance monitoring, and risk modeling. - Can AI replace human advisors?
No — it complements them. Humans still lead in trust, ethics, and complex decision-making. - How does AI affect me personally?
It decides credit approvals, sends fraud alerts, and tailors banking offers — often without you noticing. - Is AI in finance always safe?
It improves security, but risks like bias, opacity, and systemic errors exist. - What is explainable AI (XAI)?
XAI ensures algorithms can justify their decisions in human terms, critical for trust. - Can AI predict stock prices?
It detects patterns but cannot guarantee returns. Markets are influenced by unpredictable factors. - Who regulates AI in finance?
SEC (USA), FCA (UK), RBI (India), and global bodies like IMF and BIS. - What is the role of robo-advisors?
They automate financial planning at scale, improving inclusion and lowering costs. - What’s next after AI?
The fusion with blockchain and quantum computing may redefine finance in the coming decade.
Disclaimer
This article is provided for informational and educational purposes only. It does not promote or encourage unlawful activity. The content is based on publicly available information and established cybersecurity practices, and every effort has been made to ensure accuracy. Technical causes described are possible scenarios based on best practices and may not represent confirmed findings of any ongoing investigation. For any legal, financial, or technical decisions, readers are advised to consult their own qualified legal, financial, or professional advisors.



